 Scientific Bulletin – Automotive Series
Scientific Bulletin – Automotive Series
 Scientific Bulletin – Automotive Series
Scientific Bulletin – Automotive Series
Year XXX, Volume 34
Alexandra IORDACHE-SABO, Ștefan VOLOACĂ
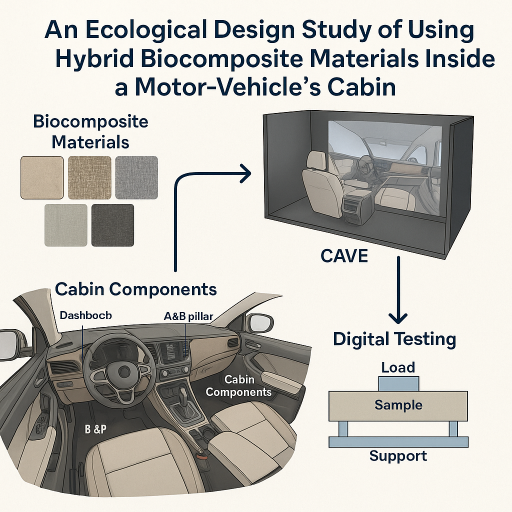
Abstract:The paper presents the analysis of the driver and the occupants’ perception in the case of using composite materials to some cabin components. There were analyzed four biocomposite materials with reinforcements of wool, wool & cotton, bamboo and bamboo & cotton. They were analyzed for the dashboard, door panels and A&B pillar using a part of an ecological design – CAVE (Cave Automatic Virtual Environment). Having the four types of biocomposite materials it was necessary to determine their properties like color, texture, grain, bump, material flakes and emissivity, all of them with a special scanner. The data was uploaded into the Deltagen software to analyze every component at a real-life scale. The CAVE made possible analyzes of different light environment conditions, the grain, colors, shines, and the reflections to windshield, windows or mirrors. Thus, with the CAVE was done a digital testing by changing materials of the components in a short amount of time and with low costs. In the Beginning of Life of a vehicle, by using the CAVE and biocomposite materials for motor vehicles’ components it is possible to obtain clean and sustainable product development.

Danut MARINESCU, Cristian Liviu POPESCU, Liviu CĂLIN, Nicuşor MIERLOIU
Abstract:The paper presents the electric concept 4WD type, DUSTER Z.E.RO 4WD developed within the Alternative Propulsion Systems for Electric and Hybrid Vehicles laboratory, from Automotive Engineering Research Centre, University of Pitesti, in order to create a green and versatile electric all-wheel drive. This concept car was built on the platform DACIA DUSTER 4WD by implementing a new electric equipment that contains Renault ZE components already launched on the market for commercialized vehicles: Renault Kangoo Z.E and Renault Fluence Z.E. The electric drive, mono-motor type includes a synchronous electric motor type placed transversely, 44 kW, a gears’ reducer with two speeds: L- Low for all terrain and H- High for the road and a mechanical all-wheel drive system. The driver to choose from three different driving modes: 2WD front-wheel drive, Auto, in which the rear-wheel drive is engaged automatically and Lock, whereby 50 % of torque is consistently fed through the rear axle. The traction battery is lithium-ion, Lithium ion Manganese Oxide (LMO) type, 400 V, 22 kWh. The estimated performances are: maximum speed: 130 km/h; autonomy NEDC (New European Driving Cycle): 130 km; standard charging: 6 to 8 hrs with home WALL BOX.
Liviu CĂLIN, Dănuț Gabriel MARINESCU, Viorel NICOLAE
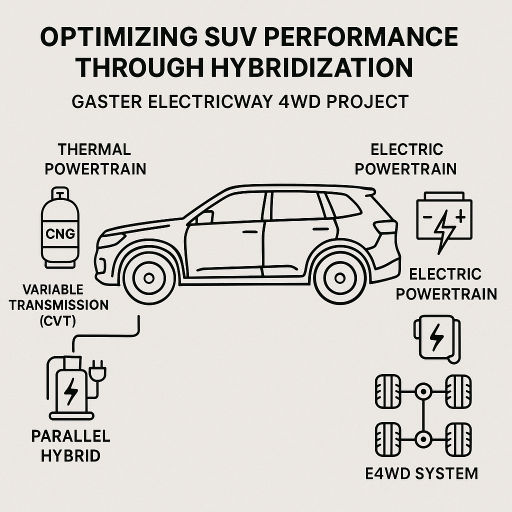
Abstract:The paper presents some of the results of the GASTER Electricway 4WD concept, developed within the Automotive Engineering Research Centre of the National University of Science and Technology POLITEHNICA Bucharest - Pitesti branch. The aim of the project was to build a Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV), by implementing a hybrid propulsion system with an electrified rear axle on the Dacia Duster model. The car has a hybrid parallel system with two shafts, organized in E4WD (Electricway 4WD) motorized solution. The thermal power train, placed in the front of the vehicle, consists in an 1.6-liter engine fueled with Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) and a CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission). The electric powertrain, located at the rear side of the vehicle, includes an electric motor coupled with a mechanical transmission, powered by a traction battery Lithium Ferro Phosphate (LFP) type.
Andreea TINTATU, Claudiu BADULESCU
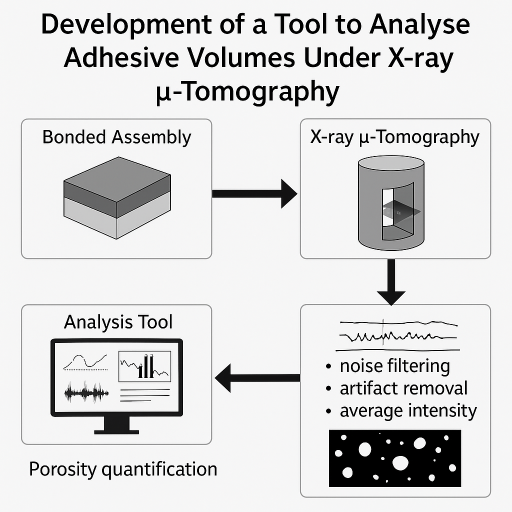
Abstract:In bonded assemblies, porosity within the adhesive layer— which often occurs during resin and hardener mixing—can significantly influence mechanical performance. This study addresses the lack of understanding regarding the effect of porosity on joint behavior by proposing a dedicated analysis methodology. A tool was developed to process X-ray μ-tomography data, allowing for noise filtering, artifact removal, and detection of microstructural entities (pores) through grayscale intensity thresholding. Two methods for average intensity extraction were designed and tested on synthetic volumes using MATLAB, with the more computationally efficient approach selected for real data analysis. This tool enables optimized porosity quantification, contributing to improved evaluation of adhesive joint integrity.
Nicoleta RACHIERU
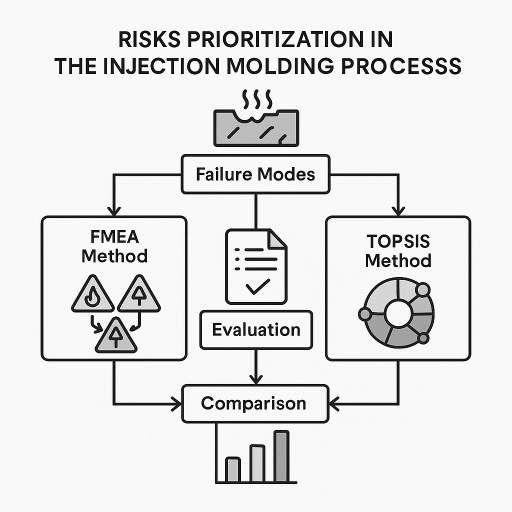
Abstract:In the automotive industry, the injection molding process is frequently used as a result of the massive market penetration of plastic products. For this reason, establishing risks and preventing them is a permanent concern of quality management and more. To prioritize these risks, a series of models and methods established by research in the field are applied. Two case studies are presented in the paper to evaluate and rank the failure modes that could occur in the plastic injection process. In the first, the classic FMEA method is used and in the second, the TOPSIS method. Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) is one of the well-known quality management techniques that is used for continuous improvement of product or process design. The approach proposed by the method is simple, but there are some limitations in obtaining a good estimate of failure rates. Thus, a new risk assessment system based on the TOPSIS theory is needed, at the end of the paper comparing the results obtained by the two methods. This paper can also serve as a guide to prevent failures of injection molded parts.
Gina-Mihaela SICOE, Daniel-Constantin ANGHEL
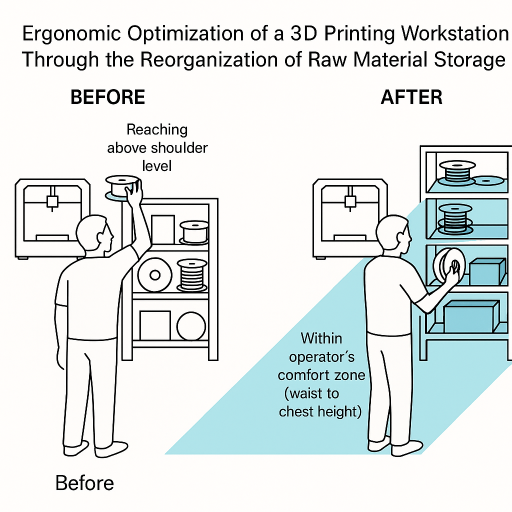
Abstract:This paper aims to analyze the ergonomic design of a workstation dedicated to the use of a 3D printer, focusing primarily on the storage and organization of raw materials used in additive manufacturing. The study is based on a real-world scenario in which the materials were initially placed randomly on shelves, without consideration for their usage frequency or weight. This disorganized arrangement led to repeated or awkward operator movements, such as reaching above shoulder level or excessive bending, which may cause discomfort or musculoskeletal disorders over time. Furthermore, this inefficient setup negatively affected operator performance. To improve the ergonomics of the workstation, we proposed a reorganization of the materials based on ergonomic principles, considering both the weight and usage frequency of the items. Heavier and less frequently used materials were relocated to the lower shelves, while lighter, frequently accessed items were positioned within the operator’s comfort zone—around waist to chest height. The goal was to reduce physical strain, enhance operational efficiency, and prevent occupational health risks. The study also includes an evaluation of the redesigned workstation using the RULA (Rapid Upper Limb Assessment) method, in order to quantify the biomechanical load in both the initial and improved configurations.
Maria-Rafaella ȘERB, Gina-Mihaela SICOE, Daniel-Constantin ANGHEL
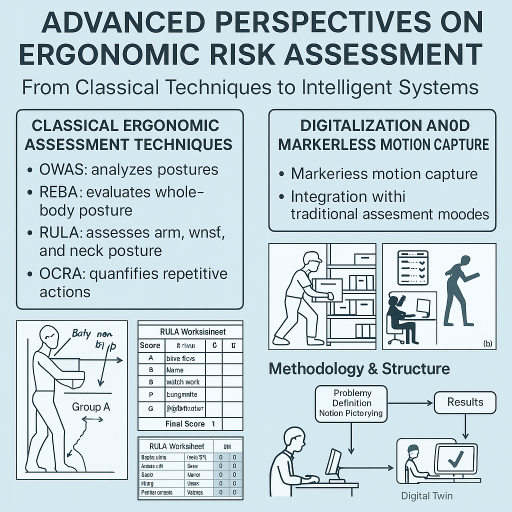
Abstract:This article critically reviews the evolution of ergonomic risk assessment methods, examining traditional evaluation techniques alongside recent innovations such as markerless motion capture systems and digital twin integration. It also explores the nature of ergonomic risks in modern industrial environments and highlights best practices and future directions for effective workplace design. The purpose is to offer a pragmatic and forward-looking framework adaptable to Industry 4.0 needs.
Ana-Cornelia GAVRILUȚĂ, Maria-Loredana PROISTOSESCU
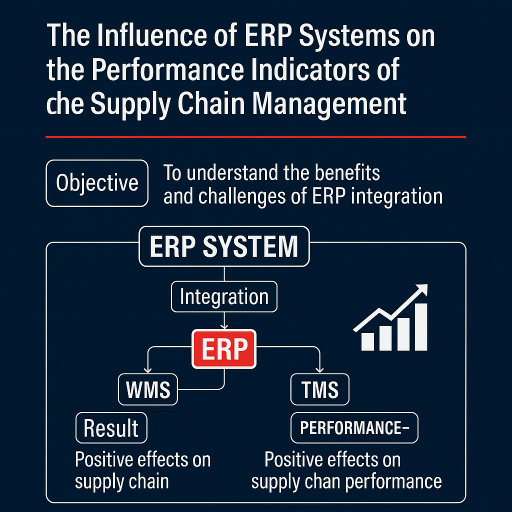
Abstract:ERP producers claim that their products have been tested and established due to lots of experiences and this important issue makes them capable of offering extraordinary solutions for various parts of the industry and services. A lot of research is currently being done on the impact of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems on business performance. The results show that after implementation of the ERP system, many benefits in terms of performance were generally achieved, but also that some benefits previously associated with the ERP system were not fully achieved. In this context the aim of this of this study is to understand the benefit and challenges associated with the integration between ERP systems and supply chain management..
Mihai ŞTIROSU, Ştefan TABACU
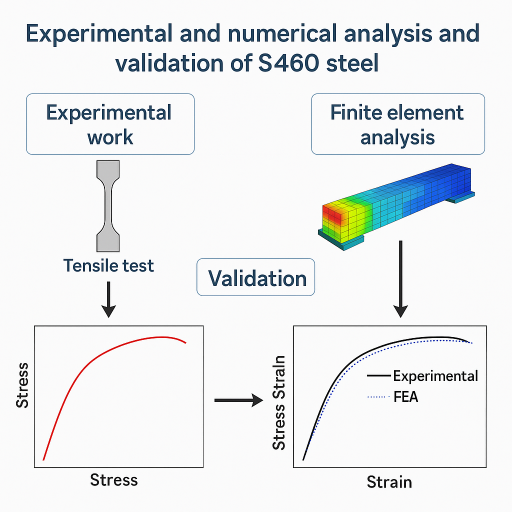
Abstract:Finite elements simulation benefit from a considerable decrease in the associated expenses with an optimal design of components. Numerical models are an efficient tool for performance evaluation, monitoring of structures, damage detection, prediction of service life, and identification of optimal maintenance methods. The success of these numerical predictions is dependent on the quality of the constitutive model adopted for material. When assessing the ultimate resistance of components as fracture as a failure mode, the use of cumulative damage models is required to provide reliable results.